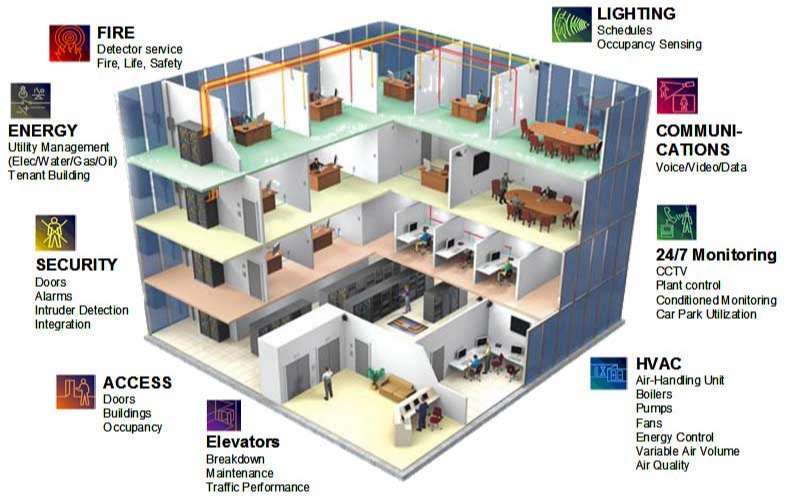
Smart Technologies in Construction
Smart Technologies in Construction: Transforming the Industry
Introduction: The construction industry is undergoing a significant transformation, largely driven by the integration of smart technologies. These technologies enhance productivity, improve safety, streamline operations, and reduce costs, while also promoting sustainability and increasing the overall efficiency of construction projects. As buildings and infrastructure become more complex, smart technologies offer innovative solutions that allow for better project management, higher quality construction, and more efficient use of resources.
In this article, we will explore the key smart technologies shaping the construction industry today, their benefits, and how they are being implemented across various stages of construction—from design to operation.
1. What Are Smart Technologies in Construction?
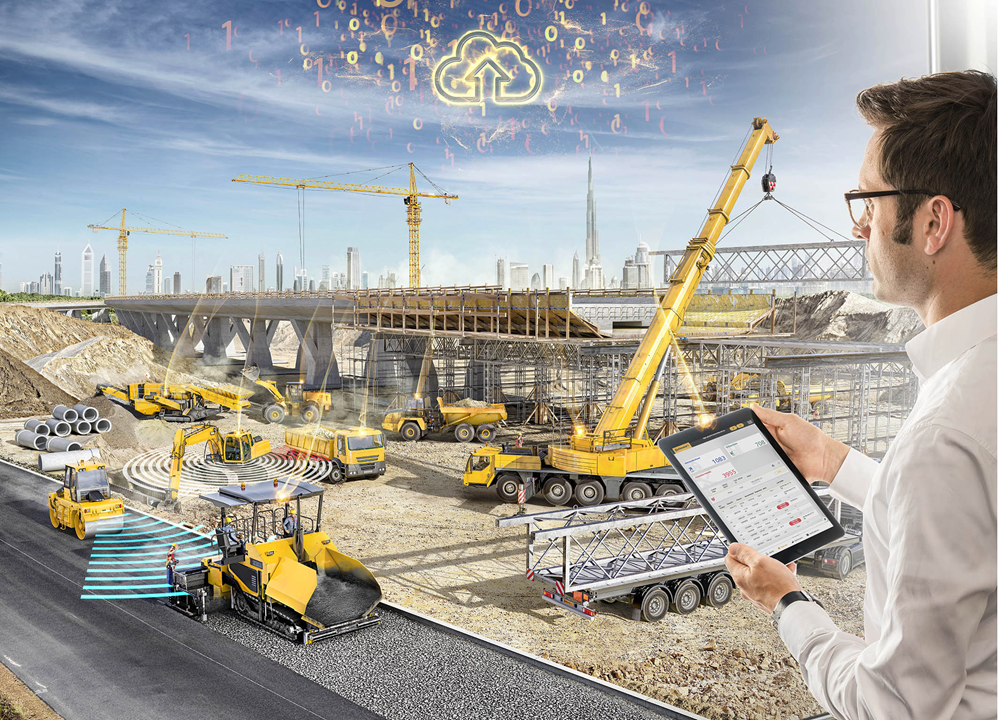
Smart technologies in construction refer to the use of advanced digital tools, automated systems, and data-driven solutions to improve the planning, design, construction, and management of buildings and infrastructure. These technologies integrate the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), robotics, automation, and data analytics into construction workflows.
The use of these technologies allows for greater accuracy, real-time monitoring, predictive maintenance, and better decision-making throughout the lifecycle of a project. Smart technologies also help reduce human error, increase safety on the job site, and optimize energy efficiency in both construction processes and the final built asset.
2. Key Smart Technologies in Construction
1. Building Information Modeling (BIM)
Building Information Modeling (BIM) is one of the most significant advancements in construction technology. BIM is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a building or infrastructure. It involves creating and managing a 3D model that contains detailed information about materials, dimensions, structural elements, systems (HVAC, electrical, plumbing), and other key aspects of a building.
- Benefits:
- Collaboration: BIM improves collaboration between architects, engineers, contractors, and owners by creating a centralized model that all stakeholders can access and update in real-time.
- Accuracy: By visualizing the entire project in 3D, BIM helps identify potential issues before construction begins, reducing errors and change orders during the build phase.
- Cost and Time Savings: BIM helps optimize the design and construction process, resulting in more accurate cost estimates and schedules, reducing waste, and speeding up project timelines.
2. Internet of Things (IoT) in Construction
The Internet of Things (IoT) refers to the network of interconnected devices that communicate with each other and exchange data. In construction, IoT sensors can be embedded in equipment, materials, or even the building structure itself to monitor performance, conditions, and environmental factors.
- Applications:
- Asset Tracking: IoT sensors are used to track tools and equipment on construction sites, ensuring they are where they are needed and reducing loss or theft.
- Real-time Monitoring: Sensors embedded in machinery or construction materials can monitor temperature, humidity, vibration, and other parameters, providing real-time data that helps optimize performance and prevent equipment failure.
- Safety: IoT-enabled wearable devices can monitor worker health and safety in real time, alerting site managers to potential hazards, such as exposure to extreme temperatures, fatigue, or unsafe conditions.
3. Drones (Unmanned Aerial Vehicles, UAVs)
Drones are increasingly used in construction for surveying, mapping, and monitoring construction sites. Equipped with high-resolution cameras and LiDAR sensors, drones provide real-time aerial imagery and data that can be processed into 3D models and used for project planning and progress monitoring.
- Applications:
- Site Surveys: Drones can quickly capture accurate topographic data, reducing the time and cost of manual surveys.
- Progress Monitoring: Drones are used to track the progress of construction in real time by providing updated aerial imagery and comparing it to the original plans.
- Safety Inspections: Drones can be used to inspect hard-to-reach or hazardous areas, such as tall buildings, rooftops, and bridges, without putting workers at risk.
4. Robotics and Automation
Robotics and automation technologies are revolutionizing many aspects of the construction industry, from bricklaying to site clearing. Robots are designed to perform repetitive, labor-intensive tasks that would typically require human labor, improving efficiency and safety.
- Applications:
- Robotic Bricklaying: Robots like the Hadrian X can lay bricks with precision, reducing construction time and labor costs.
- 3D Printing: 3D printers are being used to create building components, structures, and even entire homes, offering a more sustainable and cost-effective method of construction.
- Automated Machinery: Automated construction equipment, such as bulldozers, cranes, and excavators, can perform tasks autonomously, reducing the need for manual labor and minimizing human error.
5. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)
AI and machine learning technologies are being applied in construction to analyze large datasets, improve decision-making, and predict outcomes. These technologies can analyze historical data to optimize project planning, scheduling, and resource allocation.
- Applications:
- Predictive Analytics: AI can predict potential delays, cost overruns, or risks based on past project data, helping to make proactive decisions and mitigate risks.
- Project Scheduling and Optimization: AI-based tools can analyze scheduling data and suggest optimizations to reduce project timelines and resource utilization.
- Construction Site Safety: AI-powered cameras and sensors can monitor construction sites for safety violations, ensuring compliance with safety regulations and reducing accidents.
6. Smart Wearables
Wearable devices, such as smart helmets, safety vests, and wristbands, are becoming increasingly popular in construction for monitoring the health and safety of workers. These devices often include sensors that track a worker's movements, monitor vital signs, and provide real-time alerts.
- Applications:
- Health Monitoring: Wearables can monitor workers' heart rate, temperature, and fatigue levels to help prevent health issues like heat stress or exhaustion.
- Location Tracking: Some wearables can track the location of workers in real time, improving site safety by ensuring that workers are not in hazardous areas during dangerous tasks.
- Safety Alerts: Wearables can send alerts if a worker falls, or if hazardous conditions are detected, such as exposure to toxic gases.
7. Smart Building Materials
Advancements in materials science have led to the development of smart building materials that can respond to environmental changes or improve the energy efficiency of a building. These materials can be integrated into construction projects to create more sustainable and resilient structures.
- Applications:
- Self-Healing Concrete: Concrete with embedded bacteria that can "heal" cracks when they appear, improving the longevity of structures.
- Phase-Change Materials (PCMs): These materials can store and release heat to help regulate a building’s temperature, improving energy efficiency and reducing heating and cooling costs.
- Smart Glass: Glass that can change its transparency or tint based on temperature, sunlight, or user preferences, helping to optimize natural lighting and improve energy efficiency.
3. Benefits of Smart Technologies in Construction
The integration of smart technologies in construction brings a wide range of benefits, both during the construction phase and throughout the lifecycle of the building. Some of the key advantages include:
-
Increased Efficiency: Automation, robotics, and AI help speed up construction processes, reducing delays and increasing productivity. Tasks that were once time-consuming or dangerous for humans can now be handled by machines or robots.
-
Cost Savings: By reducing material waste, optimizing resource allocation, and improving project timelines, smart technologies help reduce overall project costs. For instance, BIM reduces errors and rework, while AI improves scheduling accuracy, leading to more predictable and cost-effective projects.
-
Enhanced Safety: Smart wearables, drones, and AI-powered safety systems help monitor and mitigate risks on construction sites, leading to fewer accidents and safer working conditions for laborers.
-
Improved Quality Control: Technologies like BIM, AI, and real-time monitoring systems provide greater visibility into the construction process, ensuring that the final product meets quality standards and is delivered as per the design specifications.
-
Sustainability: Many smart technologies contribute to energy-efficient and sustainable construction practices. From reducing material waste to optimizing energy use in buildings, these technologies help meet environmental goals and comply with green building certifications (e.g., LEED).
-
Better Project Management: Real-time data and predictive analytics allow for better decision-making, helping to manage costs, schedules, and resources more effectively. This leads to more successful project delivery, even under tight constraints.
4. Challenges and Considerations
While the benefits of smart technologies in construction are clear, there are also challenges that need to be addressed:
-
High Initial Costs: Implementing smart technologies often requires significant upfront investment in hardware, software, and training.
-
Integration with Legacy Systems: Many construction companies still rely on traditional methods and systems, and integrating new technologies with existing workflows can be challenging.
-
Skill Gap: There is a need for skilled workers who are capable of operating and maintaining these advanced technologies, creating a potential skills gap in the workforce.
-
Data Privacy and Security: As construction sites become more connected, the volume of data generated increases. Managing this data securely and ensuring that sensitive information is protected is an ongoing challenge.
5. Conclusion
Smart technologies are revolutionizing the construction industry, offering innovative solutions that improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance safety, and support sustainability. The adoption of technologies like BIM, IoT, robotics, AI, and smart materials is helping to streamline construction processes and create more resilient, energy-efficient buildings. While the transition to these technologies presents challenges, the long-term benefits they provide make them a crucial component of the future of construction. As the industry continues to embrace digital transformation, smart technologies will play an even greater role in shaping the built environment.