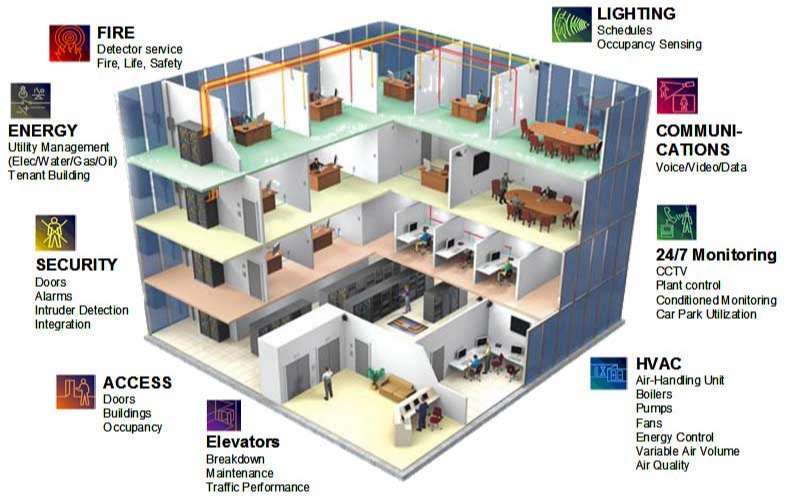
Energy Management and Energy Saving
Energy management and energy saving are key for
sustainability, cost reduction, and environmental responsibility. With rising
energy costs and climate concerns, efficient energy use is increasingly
important. Energy management optimizes energy consumption through strategies,
technologies, and policies, while energy saving reduces unnecessary energy use
without affecting comfort or performance.
Understanding Energy Management
Energy management is a systematic approach to monitoring, controlling, and
optimizing energy use in buildings or organizations. It combines planning,
implementation, and ongoing evaluation to reduce consumption while maintaining
performance and comfort.
Key elements include:
- Energy
Monitoring and Audits: Assess consumption patterns and identify
inefficiencies.
- Energy
Data Analysis: Understand usage patterns and prioritize initiatives.
- Setting
Energy Goals: Define targets based on audits and analysis.
- Energy
Efficiency Measures: Upgrade equipment, optimize HVAC, and use efficient
lighting.
- Employee
Engagement: Train staff and promote energy-saving practices.
- Continuous
Improvement: Monitor results and identify further savings.
Energy Saving Strategies
Energy saving involves reducing consumption through behavioral changes,
technology, and efficient practices:
- Upgrade
Equipment: Use energy-efficient lighting, HVAC, and appliances.
- Building
Insulation and Sealing: Prevent energy loss through proper insulation and
sealing.
- Smart
Controls and Automation: Implement smart meters, thermostats, and BAS for
optimized energy use.
- Behavioral
Changes: Encourage staff and occupants to adopt energy-efficient habits.
- Optimize
Industrial Processes: Streamline operations, recover waste heat, and use
efficient motors.
- Renewable
Energy Integration: Incorporate solar, wind, or geothermal energy.
Benefits
Implementing energy management and saving strategies offers:
- Cost
Savings: Lower energy bills and ROI from efficiency upgrades.
- Environmental
Impact: Reduce carbon footprint and emissions.
- Improved
Comfort and Productivity: Optimize lighting, temperature, and air quality.
- Regulatory
Compliance and Incentives: Meet regulations and benefit from incentives.
- Energy
Security: Reduce reliance on external energy sources.
Challenges
- Upfront
Costs: Initial investment may be high but offset by long-term savings.
- Resistance
to Change: Training and awareness are needed to overcome reluctance.
- Technological
Integration: Smart systems require proper setup and expertise.
Energy management and saving are vital for cost reduction, sustainability, and
occupant comfort. Through energy audits, building services commissioning, and
strategic efficiency measures, organizations can significantly reduce energy
consumption while contributing to a greener future.